Table of Contents
Dogs rely on their teeth for much more than just eating. Teeth play a major role in chewing, playing, grooming, and overall health. Just like humans, dogs go through different dental stages as they grow, starting with baby teeth and eventually developing a full set of adult teeth. Many dog owners are surprised to learn that dogs actually have more teeth than humans once fully grown.
Understanding how many teeth dogs have, what each type of tooth does, and how dental health impacts your dog’s life can help you take better care of your pup. Whether you have a young puppy or a senior dog, knowing what’s normal when it comes to teeth makes it easier to spot problems early.
How Many Teeth Do Puppies Have?
Puppies are born without teeth. During the first few weeks of life, they rely completely on their mother’s milk for nutrition. Puppy teeth, also called deciduous teeth or baby teeth, begin to emerge when puppies are about 2 to 4 weeks old.
By the time a puppy is around 6 to 8 weeks old, they usually have a full set of 28 baby teeth. These teeth are small, sharp, and designed to help puppies transition from nursing to solid food.
Puppy teeth are not meant to last forever. They serve as placeholders for adult teeth and help puppies learn how to chew and explore the world.
How Many Teeth Do Adult Dogs Have?
Once a dog reaches adulthood, they will have 42 permanent teeth. This is significantly more than humans, who typically have 32 adult teeth.
Adult dog teeth usually finish coming in between 6 and 8 months of age. During this time, puppies lose their baby teeth as adult teeth push through the gums. It’s common for owners to find small teeth on the floor or stuck in toys, but many puppies swallow their baby teeth without issue.
According to the American Veterinary Dental College, 42 teeth is the normal number for a healthy adult dog.
https://avdc.org/resources/dog-owner-resources/
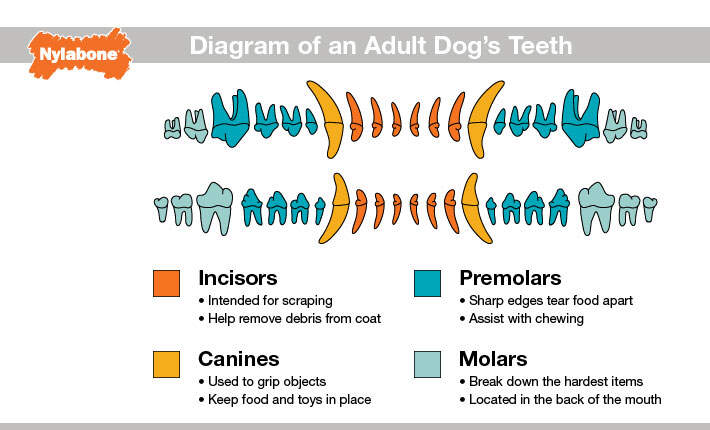
Types of Dog Teeth and What They Do
Dogs have four different types of teeth, and each type plays a specific role in eating and daily activities.
Incisors
Dogs have 12 incisors, six on the top and six on the bottom. These are the small teeth located at the very front of the mouth. Incisors are used for nibbling, grooming, and picking up objects. Dogs often use them to gently remove dirt from their fur or to scrape meat from bones.
Canines
Dogs have 4 canine teeth, also called fangs. These are the long, pointed teeth located next to the incisors. Canines are used for gripping, tearing, and holding objects. They are especially important for play, defense, and carrying toys.
Premolars
Dogs have 16 premolars, eight on the top and eight on the bottom. Premolars help dogs chew and break down food. These teeth are also used during play when dogs chew on toys or treats.
Molars
Dogs have 10 molars, which are located at the back of the mouth. Molars are flat and strong, designed for grinding food. They help dogs break down kibble and tougher foods before swallowing.
Together, these 42 teeth allow dogs to eat efficiently and interact with their environment.
When Do Puppies Lose Their Baby Teeth?
Most puppies begin losing their baby teeth around 3 to 4 months old. This process usually continues until they are about 6 months old. During this time, puppies may chew more than usual because their gums feel sore or itchy.
Teething is completely normal, but it can be uncomfortable. Providing safe chew toys helps puppies relieve discomfort and prevents them from chewing on furniture or shoes.
Helpful teething toys recommended by veterinarians include rubber or nylon chews made specifically for puppies:
https://www.akc.org/expert-advice/health/puppy-teething/
What Happens If a Dog Has Missing Teeth?
Some dogs naturally lose teeth due to genetics, injury, or dental disease. Missing teeth are more common in small breeds and older dogs, but they can happen at any age.
Dogs can usually live normal, happy lives with missing teeth, especially if they receive proper care. However, missing teeth may indicate underlying dental problems such as gum disease or infection.
If your dog is missing teeth or has loose teeth, it’s important to have a veterinarian examine their mouth to rule out pain or disease.
Why Dental Health Is So Important for Dogs
Dental health affects much more than your dog’s mouth. Poor oral hygiene can lead to plaque buildup, tartar, and gum disease, which can cause pain, bad breath, and tooth loss. Bacteria from infected gums can also enter the bloodstream and affect the heart, liver, and kidneys.
According to veterinary studies, over 80% of dogs show signs of dental disease by age three.
https://www.petmd.com/dog/general-health/dog-dental-care
Regular dental care helps dogs stay healthier, more comfortable, and happier throughout their lives.
Signs of Dental Problems in Dogs
Dogs often hide pain, so dental problems can go unnoticed until they become serious. Common signs include bad breath, red or bleeding gums, yellow or brown buildup on teeth, difficulty eating, drooling, and pawing at the mouth.
Some dogs may stop chewing toys or avoid hard food if their teeth hurt. If you notice any of these signs, a veterinary checkup is recommended.
How to Take Care of Your Dog’s Teeth
Dental care should start early, even when dogs are puppies. Brushing your dog’s teeth regularly is one of the most effective ways to prevent dental disease. Using dog-safe toothpaste and a soft toothbrush helps remove plaque before it hardens into tartar.
Dental chews, water additives, and specially formulated dog food can also support oral health. However, these products work best when combined with brushing.
The Veterinary Oral Health Council provides a list of approved dental products for dogs:
https://vohc.org/accepted-products/
Professional Dental Cleanings for Dogs
Even with good at-home care, most dogs eventually need professional dental cleanings. These cleanings are performed by veterinarians and involve removing tartar above and below the gumline.
Professional cleanings help prevent infections, tooth loss, and long-term health issues. Your veterinarian can recommend how often your dog needs dental cleanings based on age, breed, and oral health.
How Dog Teeth Affect Behavior and Play
Healthy teeth are important for play and social interaction. Dogs use their mouths during play with other dogs, carrying toys, and chewing treats. Dental pain can make dogs irritable or less interested in play.
At Woof Playcare, dogs engage in supervised play, and healthy teeth help ensure safe, comfortable interactions. Dogs with dental pain may chew less, avoid toys, or show changes in behavior.
Frequently Asked Questions About Dog Teeth
How many teeth does a puppy have?
Puppies have 28 baby teeth once fully developed.
How many teeth does an adult dog have?
Adult dogs have 42 permanent teeth.
Is it normal for puppies to swallow their baby teeth?
Yes. Most puppies swallow their baby teeth while eating or playing, and it is harmless.
When should I start brushing my dog’s teeth?
You can start gentle brushing as soon as your puppy is comfortable with handling, usually around 8–12 weeks old.
Do all dogs lose teeth as they age?
No. Tooth loss is not normal aging and usually indicates dental disease or injury.
Can dental problems affect my dog’s overall health?
Yes. Dental disease can lead to infections that affect the heart, kidneys, and other organs.
Dogs Have More Teeth Than Many People Realize
Dogs have more teeth than many people realize, and each tooth plays an important role in eating, playing, and staying healthy. Puppies start with 28 baby teeth and eventually grow a full set of 42 adult teeth by the time they reach maturity. Understanding your dog’s dental development helps you spot problems early and provide better care.
Good dental health leads to better overall health, more energy, and happier playtime. Whether your dog is a playful puppy or a senior companion, taking care of their teeth is one of the best ways to support a long, healthy life.